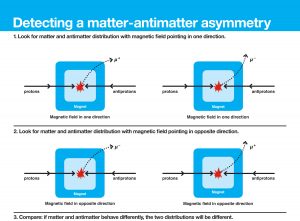
The DZero result is based on the comparison of the distributions of positively and negatively charged muons (μ+ and μ-) emerging from high-energy proton-antiproton collisions produced by the Tevatron particle collider. A strong magnetic field inside the DZero particle detector forces the muons that emerge from those collisions to travel along a curved path. Two muons with opposite charge follow paths that curve in opposite direction (see graphic). Scientists first compared the muon distributions when the the magnetic field inside the DZero detector pointed in one direction (configuration 1) and then compared their distributions when the magnetic field had been reversed (configuration 2). If the matter-antimatter symmetry were perfect, the comparison of the muon distributions in the two configurations would yield the same result. Instead, the DZero experiment observed a one-percent deviation, evidence for a matter-antimatter asymmetry. Credit: Fermilab