During the manufacturing process, many medical devices or equipment for use on humans must be sterilized according to recognized standards. This includes gowns, surgical drapes, syringes and implantable medical devices. In fact, the United States has a huge medical device sterilization industry, regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The industry is expected to grow considerably in the coming years.
The most common medical device sterilization methods will unlikely be able to handle that continued growth, say experts in the field. In addition, the industry is looking for alternatives since the two leading technologies use substances—ethylene oxide and cobalt-60—that present safety issues.
Researchers at U.S. Department of Energy’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory believe they can help. Using funding provided by the National Nuclear Security Administration, Fermilab researchers are building a prototype electron beam accelerator that integrates four emerging accelerator technologies into a single, efficient accelerator system. Industrial partners could use such a machine to make X-rays for sterilizing equipment.
“The focus of our effort is to develop a high-power electron beam that can serve as an alternative to large-scale cobalt facilities,” said Thomas Kroc, applications physicist and principal investigator of the Fermilab medical device sterilization efforts. “In doing that, we exploit the superconducting accelerator experience that we developed here at Fermilab. We think that technology provides the efficiency that makes it feasible to run electron accelerators that can sterilize medical equipment as well as existing large facilities that use other methods.”

Researchers at Fermilab are developing a new type of electron accelerator ideal for creating X-rays to sterilize medical equipment, including gowns, gloves and other protective equipment. Photo: aslysun/Shutterstock
Evolving sterilization methods
Electron beams first were used to sterilize medical equipment in the late 1950s, but their use was hampered by equipment reliability issues. Instead, gamma rays—high-energy photons produced by the radioactive decay of cobalt-60—became the go-to radiation sterilization technology. Since that time, and especially in the last decade, electron beam technology and X-ray technology have vastly improved. Kroc believes they now are viable alternatives to gamma rays. Fermilab received NNSA funding to look into the development and commercialization of these alternatives.
Today, around 50% of medical devices in the United States are sterilized using ethylene oxide, which is a colorless gas that kills microorganisms. It is extremely effective at sterilizing heat- or moisture-sensitive medical equipment without damaging it. Much of the remainder, around 40%, are sterilized using ionizing radiation like gamma rays created from cobalt-60, a radioactive isotope of cobalt. The rest use X-rays or electron beams.
Health and environmental concerns regarding the use of the highly regulated ethylene oxide are driving a search for alternatives. The use of radioactive isotopes like cobalt-60 is not a good alternative as it presents health and national security concerns. It also has practical issues such as how to transport and dispose of the residual radioactive waste safely and efficiently. In addition, there is a worldwide shortage of cobalt itself.
The NNSA Office of Radiological Security has been promoting the use of alternative technologies, including electron beams, for radiation sterilization to reduce U.S. reliance on cobalt-60. Given its strong foundation in particle beam technology, Fermilab is a leader in this effort.
Medical device sterilization with cobalt is performed on a large scale because of the penetrative power of the gamma rays that cobalt creates. The gamma rays can traverse and sterilize pallets full of medical equipment.
X-rays offer penetration as effective as gamma rays. Scientists can operate electron beam accelerators and force the electrons to emit X-rays without creating the residual waste associated with gamma-ray production. But the current accelerator technology for these systems is not energy—and hence cost—efficient.
The Fermilab team aims to change that. They work on developing a new type of electron beam accelerator system. At the core of their system is a superconducting radio frequency cavity that is used to propel charged particles. Their key to creating a more efficient accelerator system is managing the cavity’s heat budget.
Combining multiple emerging technologies
The typical SRF cavity used in most science facilities today is made of niobium. It requires liquid helium to keep it cold enough to conduct electric currents without resistance, the hallmark of superconducting material. Rather than building a helium liquification plant and all the associated infrastructure, the innovative design developed at Fermilab uses commercially available cryocoolers. These are also used in MRI machines, which need cooling for their superconducting magnets. But to keep the heat produced by equipment within a level that the cryocoolers can handle, the total heat generated by the system during operation must be within approximately five watts—less than the heat typically created by a light bulb.
To stay within that limit, the Fermilab team combines four technologies. Each of these has been independently demonstrated to work. Their prototype will integrate these patented technologies into an energy-efficient accelerator system.
First, they use niobium SRF cavities coated with tin, which increases the operating temperature of the superconducting cavity and puts it within a cryocooler’s operating range. Next, they embed the source of the electrons, the beam gun, directly into the cavity rather than transporting the electron beam from an external source via a transport line. This minimizes the amount of external heat that can leak into the superconducting cavity system. Similarly, they designed the coupler that transfers the radio frequency power into the cavity to minimize the amount of heat that can enter from the outside. Finally, they use conduction cooling in the commercial cryocooler and aluminum to connect the cryocooler to the SRF cavity. Together, this system will efficiently accelerate electrons to the energies needed for X-ray production.
To make X-rays, the beam from the electron accelerator is directed onto a target made of tantalum, tungsten or another heavy element. The material quickly slows down the electrons, and the particles emit X-rays in response, a process known as Bremsstrahlung radiation. The energy of the resulting X-rays is equal to the energy lost by the electrons as they slow down.
Application beyond physics
To advance the use of electron beam accelerators for medical device sterilization, Fermilab hosts an annual medical device sterilization workshop. The fifth such workshop, held Sept. 20-21, 2023 at Fermilab, brought together more than 200 stakeholders, in person and online. Participants came from Brazil, Canada, Germany and across the United States. They included representatives from major contract medical device sterilization companies, accelerator manufacturers, medical device manufacturers, academia, industrial regulators and federal regulators.
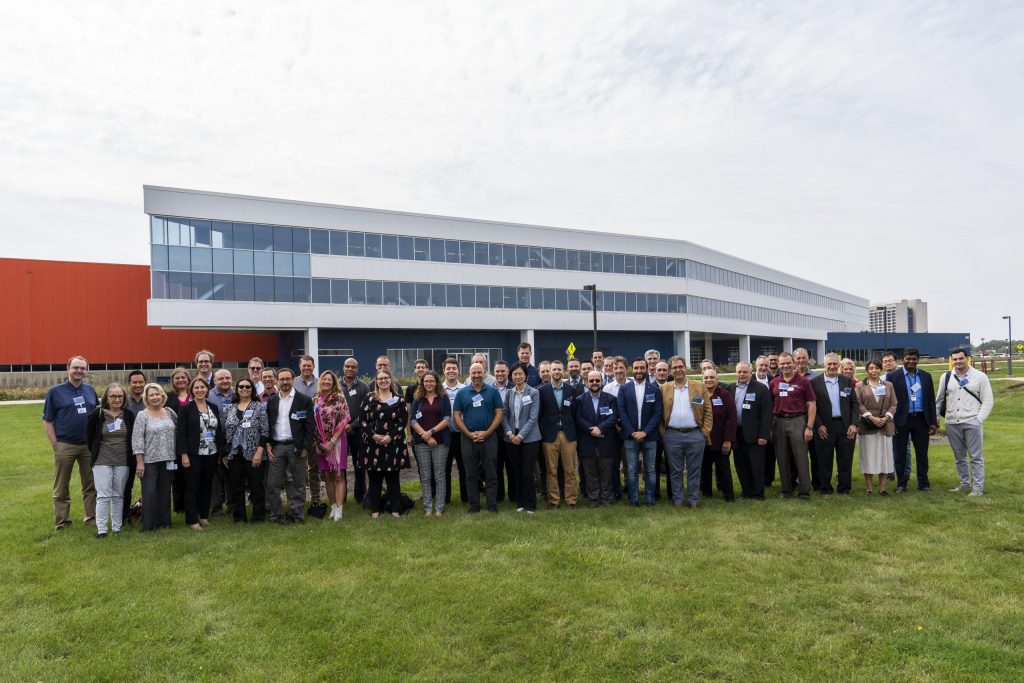

Participants at the 2023 medical device sterilization workshop at the Illinois Accelerator Research Center at Fermilab. Offering both in-person and online attendance, the workshop brought together more than 200 representatives of medical device sterilization companies, accelerator manufacturers, medical device manufacturers, academia and regulators. Photo: Dan Svoboda, Fermilab
“This workshop brings together multiple stakeholder groups; stakeholders who do not often have the opportunity to meet and discuss cross-cutting issues in a pre-competitive environment. Similarly, it gives FDA an opportunity to engage and share information with these stakeholders in a manner that we don’t really get otherwise,” said Ryan Ortega, a regulator from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration who spoke at the event.
“Participation in the workshop has been a very beneficial and positive experience for me and my FDA colleagues. We get a significant amount of actionable information and stakeholder engagement from the workshop every year,” said Ortega.
By enabling this multidisciplinary discourse, the workshop organizers aim to facilitate the switch from ethylene oxide and gamma ray-producing cobalt-60 to accelerator-based technology and lay the groundwork for commercializing this technology.
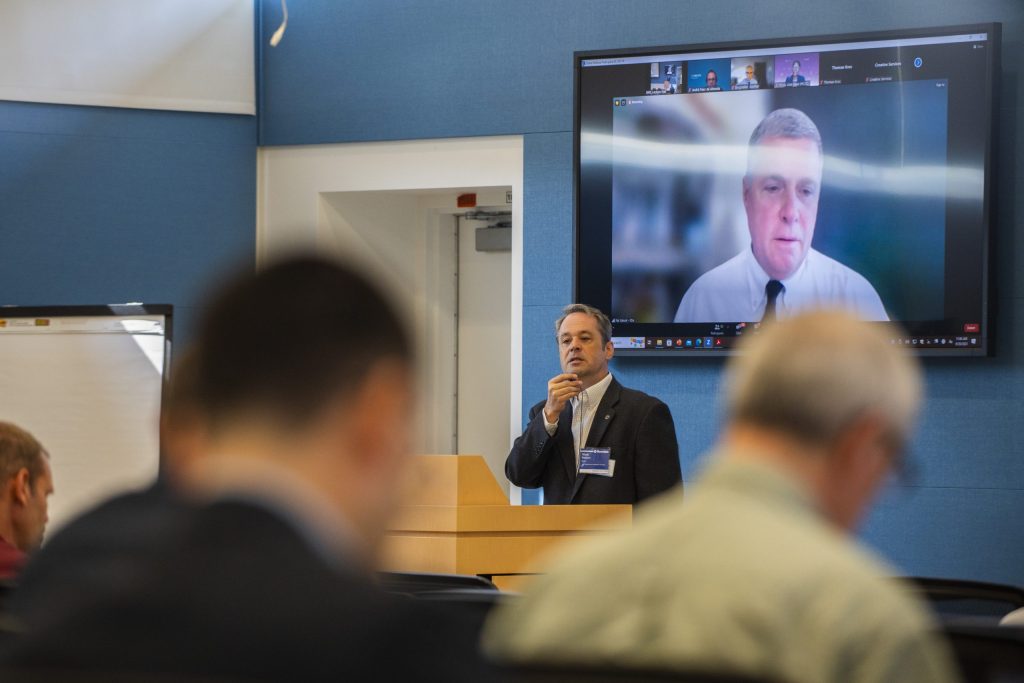

Mark Pasmore of Baxter Healthcare Corporation (center), co-initiator of the medical device sterilization workshop series along with Fermilab’s Tom Kroc, speaks at the 2023 workshop. Photo: Dan Svoboda, Fermilab
“We want to leverage Fermilab’s expertise and the power of electron beam technology to spur economic growth, foster community development, meet national security needs and create an environment of innovation,” said Fermilab’s William Pellico, director of the Illinois Accelerator Research Center. “The scientists at Fermilab who work on this emerging accelerator technology are encouraged by the NNSA support and commitment to this endeavor.”
The road to commercialization
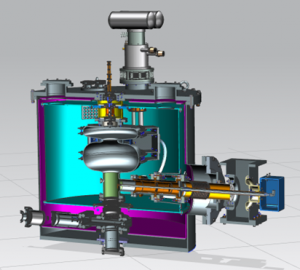
The compact design of Fermilab’s electron beam prototype accelerator for sterilizing medical equipment is made possible by combining four emerging particle accelerator technologies. Image: Gregory Langlois, Fermilab
While the technical team focuses on getting the prototype electron beam accelerator up and running, another component of the recent NNSA grant is to look at commercialization avenues.
One of the commercialization hurdles that must be overcome is the ability for small- and medium-sized companies to do accelerator-based sterilization in house. Companies are looking for cost-effective accelerator options that are sized to meet their needs.
A team of scientists and engineers at Fermilab is building a compact prototype accelerator that can propel electrons to the energy of 1.6 million electron volts and has beam power output of 20 kilowatts. The prototype will enable them to validate the integration of the various technologies they are bringing together. It also is a step toward smaller sterilization applications. The final goal is an accelerator with 7.5 MeV beam energy and 200 kW beam power, which would be a valid alternative to large cobalt-60 facilities.
“The prototype is not the final goal, but there are companies that are interested in building this kind of accelerator for small, compact, end-of-line-type use cases such as blood kit sterilization,” said Kroc. “While we’re trying to facilitate specific requests, this development also serves the industry as a whole.”
Kroc also pointed out that these accelerator-beam radiation sterilization applications are not limited to medical equipment. Representatives from the bioprocess industry, which makes single-use systems for manufactures of vaccines and pharmaceuticals, participated in the Medical Device Sterilization Workshop. They are users of gamma-ray sterilization who are looking to transition to X-rays.
Once the 1.6-MeV prototype is built and tested, Kroc expects to hold a workshop specifically for companies and industries that have the potential of being commercialization partners. “We’ll present our progress and results and get feedback on whether we’re meeting their demand, what adjustments we might have to make, and then try to stimulate further interest,” said Kroc.
The Illinois Accelerator Research Center, also known as IARC, was established with support from the State of Illinois to industrialize Fermilab’s technologies and, together with other partners, to advance the next generation of technologies, products and applications to assist U.S. industry and support the U.S. Department of Energy’s science mission.
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
