ArgoNeuT sheds light on electron neutrino interactions
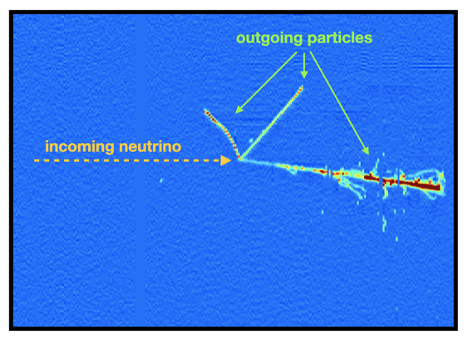
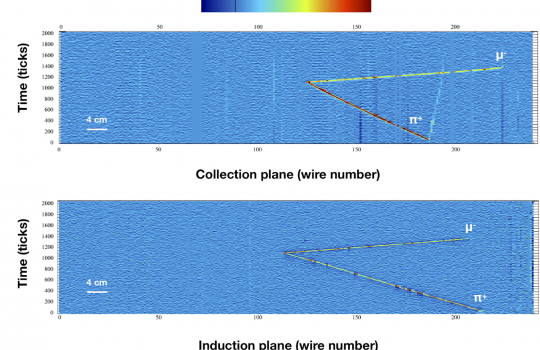
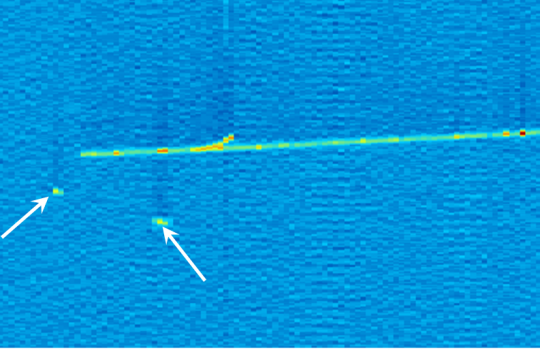
The ArgoNeuT collaboration has published new measurements of the neutrino interaction channel critical for future experiments that seek to understand the difference between matter and antimatter in the world of neutrinos. Their paper presents new strategies for identifying electron neutrinos in liquid-argon neutrino detectors like ArgoNeuT.