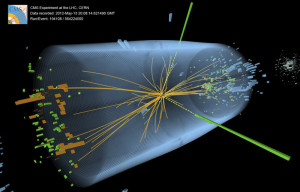
CMS Higgs Event Graphic – The discovery of the Higgs particle in 2012 was named breakthrough of the year by Science magazine. The CMS experiment as one of two experiments at the Large Hadron Collider that recorded telltale signs of the production of the Higgs boson in high-energy proton-proton collisions. Credit: CMS Collaboration/CERN
Editor’s note: For more information on Fermilab’s role in the hunt for the Higgs, visit this page on the Fermilab site: http://www.fnal.gov/pub/science/higgs.
The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences today awarded the Nobel Prize in physics to theorists Peter Higgs and Francois Englert to recognize their work developing the theory of what is now known as the Higgs field, which gives elementary particles mass. U.S. scientists played a significant role in advancing the theory and in discovering the particle that proves the existence of the Higgs field, the Higgs boson.
In the 1960s, Higgs and Englert, along with other theorists, including Robert Brout, Tom Kibble and Americans Carl Hagen and Gerald Guralnik, published papers introducing key concepts in the theory of the Higgs field. In 2012, scientists on the international ATLAS and CMS experiments, performed at the Large Hadron Collider at CERN laboratory in Europe, confirmed this theory when they announced the discovery of the Higgs boson.
Nearly 2000 physicists from U.S. institutions—including 89 U.S. universities and seven U.S. Department of Energy laboratories—participate in the ATLAS and CMS experiments, making up about 23 percent of the ATLAS collaboration and 33 percent of CMS at the time of the Higgs discovery. Brookhaven National Laboratory serves as the U.S. hub for the ATLAS experiment, and Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory serves as the U.S. hub for the CMS experiment. U.S. scientists provided a significant portion of the intellectual leadership on Higgs analysis teams for both experiments.
“It is an honor that the Nobel Committee recognizes these theorists for their role in predicting what is one of the biggest discoveries in particle physics in the last few decades,” said Fermilab Director Nigel Lockyer. “I congratulate the whole particle physics community for this achievement.”
The majority of U.S. scientists participating in LHC experiments work primarily from their home institutions, remotely accessing and analyzing data through high-capacity networks and grid computing. The United States plays an important role in this distributed computing system, providing 23 percent of the computing power for ATLAS and 40 percent for CMS. The United States also supplied or played a leading role in several main components of the two detectors and the LHC accelerator, amounting to a value of $164 million for the ATLAS detector, $167 million for the CMS detector, and $200 million for the LHC. Support for the U.S. effort comes from the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science and the National Science Foundation.
“It’s wonderful to see a 50-year-old theory confirmed after decades of hard work and remarkable ingenuity,” said Brookhaven National Laboratory Director Doon Gibbs. “The U.S. has played a key role, contributing scientific and technical expertise along with essential computing and data analysis capabilities—all of which were necessary to bring the Higgs out of hiding. It’s a privilege to share in the success of an experiment that has changed the face of science.”
The discovery of the Higgs boson at CERN was the culmination of decades of effort by physicists and engineers around the world, at the LHC but also at other accelerators such as the Tevatron accelerator, located at Fermilab, and the Large Electron-Positron accelerator, which once inhabited the tunnel where the LHC resides. Work by scientists at the Tevatron and LEP developed search techniques and eliminated a significant fraction of the space in which the Higgs boson could hide.
Higgs and Englert published their papers independently and did not meet in person until the July 4, 2012, announcement of the discovery of the Higgs boson at CERN. Higgs, 84, is a professor emeritus at the University of Edinburgh in Scotland. Englert, 80, is a professor emeritus at Universite libre de Bruxelles in Belgium.
The prize was announced this morning at 5:45 CDT.
Fermilab is America’s premier national laboratory for particle physics research. A U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science laboratory, Fermilab is located near Chicago, Illinois, and operated under contract by the Fermi Research Alliance, LLC. Visit Fermilab’s website at www.fnal.gov and follow us on Twitter at @FermilabToday.
One of 10 national laboratories overseen and primarily funded by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Brookhaven National Laboratory conducts research in the physical, biomedical, and environmental sciences, as well as in energy technologies and national security. Brookhaven Lab also builds and operates major scientific facilities available to university, industry and government researchers. Brookhaven is operated and managed for DOE’s Office of Science by Brookhaven Science Associates, a limited-liability company founded by the Research Foundation for the State University of New York on behalf of Stony Brook University, the largest academic user of Laboratory facilities, and Battelle, a nonprofit applied science and technology organization.



