World’s best measurement of W boson mass points to Higgs mass and tests Standard Model
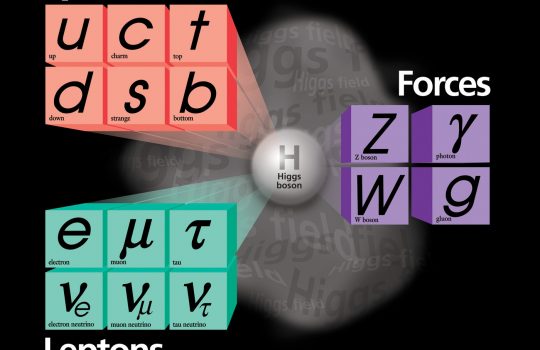
The world’s most precise measurement of the mass of the W boson, one of nature’s elementary particles, has been achieved by scientists from the CDF and DZero collaborations at the Department of Energy’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory.