New calculation refines comparison of matter with antimatter
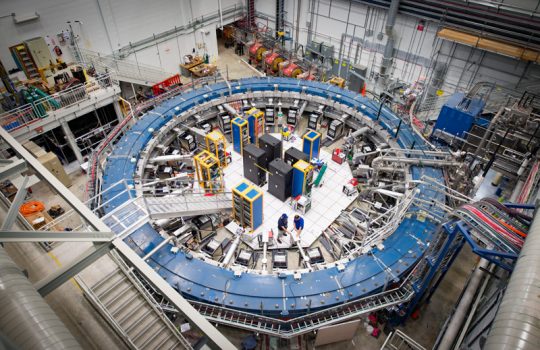
From Brookhaven National Laboratory, Sept. 17, 2020: Brookhaven theorists publish an improved prediction for the tiny difference in kaon decays observed by experiments. Understanding these decays and comparing the prediction with more recent state-of-the-art experimental measurements made at Fermilab and CERN gives scientists a way to test for tiny differences between matter and antimatter.