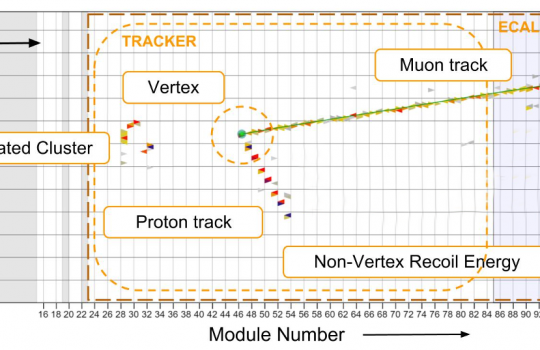
Neutrinos offer a new way to investigate the building blocks of matter
Phys.org, May 21, 2024
Over the course of three years, scientists working on MINERvA recorded more than a million interactions of antineutrinos with other particles. This data allowed scientists to finally calculate the proton’s size using neutrinos, making this a statistically significant measurement of this characteristic.