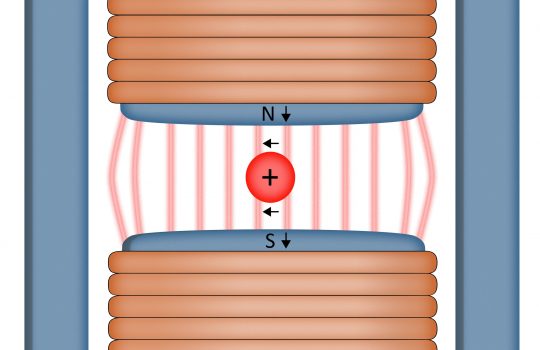
From University of Wisconsin-Madison, Sept. 28, 2020: Getting blasted with proton beams takes a toll on accelerator targets. As researchers begin to consider upgrading existing accelerators and building more powerful models, the durability of those devices is a major concern. University scientists are working with Fermilab in a new collaboration to study and improve the durability of targets and target windows, which will be important for neutrino experiments such as the international Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment, hosted by Fermilab.