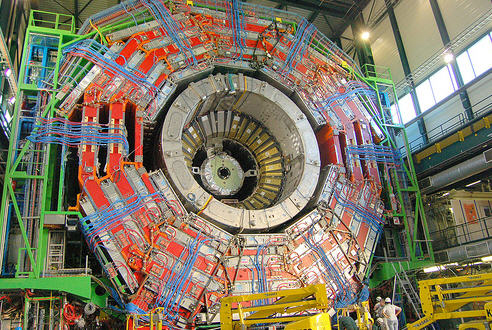
Beams are Back in the Large Hadron Collider
Particle beams are once again zooming around the world’s most powerful particle accelerator—the Large Hadron Collider—located at the CERN laboratory near Geneva, Switzerland. On November 20 at 4:00 p.m. EST, a clockwise circulating beam was established in the LHC’s 17-mile ring.