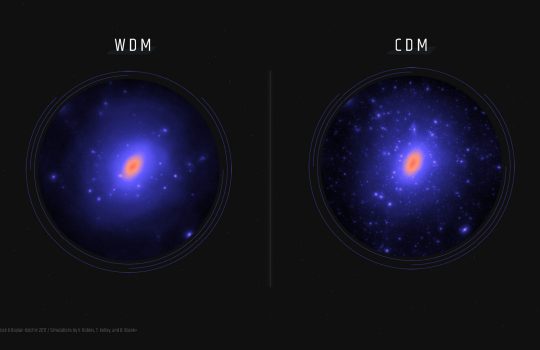
Precision measurements of intracluster light suggest possible link to dark matter
Faint light from rogue stars not bound to galaxies has been something of a mystery to scientists. The dimness of this intracluster light makes it difficult to measure, and no one knows how much there is. Scientists on the Dark Energy Survey, led by Fermilab, have made the most radially extended measurement of this light ever and have found new evidence that its distribution might point to the distribution of dark matter.