Prep work to start for DUNE-related construction at Fermilab
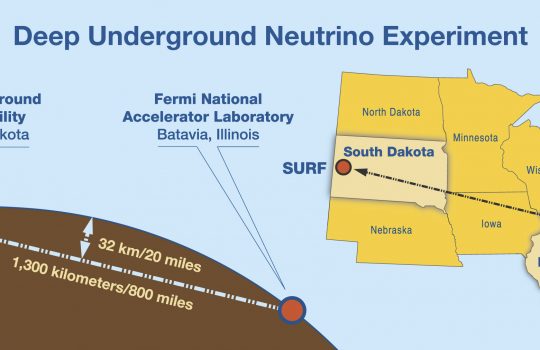
Site preparation work starts at Fermilab this fall for the international Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment. Contractors will begin site prep where the powerful particle beam will be extracted and sent toward its final destination in South Dakota.