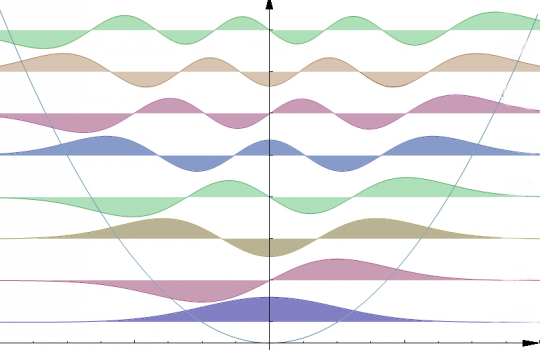
A quantum leap in particle simulation
A Fermilab group has found a way to simulate, using a quantum computer, a class of particles that had resisted typical computing methods. Their novel approach opens doors to an area previously closed off to quantum simulation in areas beyond particle physics, thanks to cross-disciplinary inspiration.