Carlos Henrique de Brito Cruz: an igniter of change
- Brazil
- Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment
- detector technology
- DUNE
- international engagement
- neutrino
- SBND
- Short-Baseline Near Detector
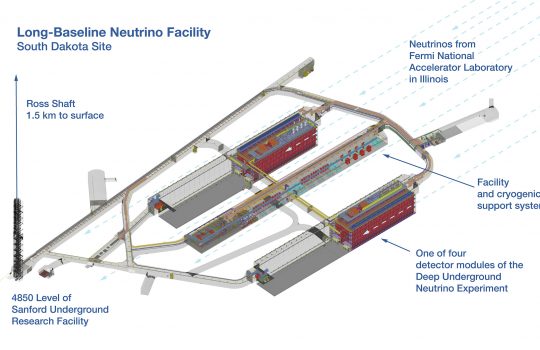
From Pesquisa, November 2020: The FAPESP scientific director shares how he encouraged behaviors that helped improve research in São Paulo. With FAPESP encouragement, researchers in Brazil have held leadership positions in international collaborations, including in a photon detection system called Arapuca. Arapuca is a technology used in Fermilab’s Short-Baseline Near Detector and a baseline technology for the international Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment, hosted by Fermilab.