Some lab magnet work proceeds on particle accelerator upgrade
- accelerator
- accelerator technology
- Berkeley Lab
- High-Luminosity LHC
- HL-LHC
- Large Hadron Collider
- LHC
- magnet
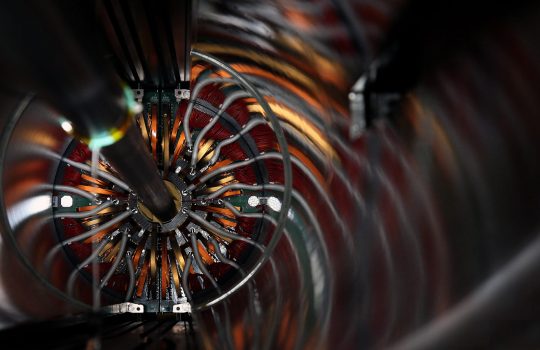
From Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, June 17, 2020: While COVID-19 risks had led to a temporary halt in fabrication work on high-power superconducting magnets built by a collaboration of three national labs for an upgrade of the world’s largest particle collider at CERN in Europe, researchers at Berkeley Lab are still carrying out some project tasks. Fermilab scientist Giorgio Apollinari, head of the U.S.-based magnet effort for the HL-LHC, is quoted in this piece.