Físicos da Unicamp são premiados nos Estados Unidos
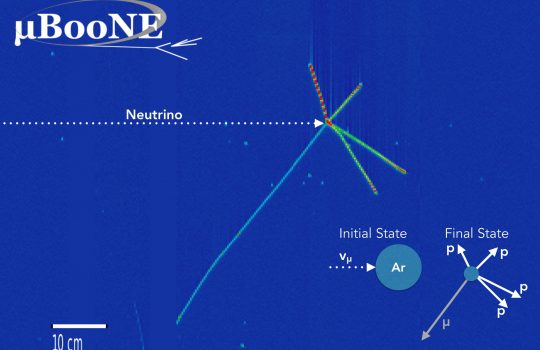
From UNICAMP, Dec. 19, 2019: Ana Amélia Machado e Ettore Segreto fazem parte da colaboração internacional Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment, sediada no Fermilab, e são responsáveis pelo detector de neutrinos chamado ARAPUCA., abreviação de Argon R&D Advanced Program Unicamp.