Dark Energy Survey census of the smallest galaxies hones the search for dark matter
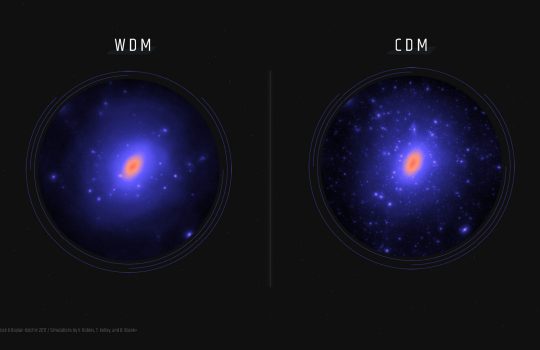
Scientists on the Dark Energy Survey have used observations of the smallest known galaxies to better understand dark matter, the mysterious substance that makes up 85% of the matter in the universe. The smallest galaxies can contain hundreds to thousands of times more dark matter than normal visible matter, making them ideal laboratories for studying this mysterious substance. By performing a rigorous census of small galaxies surrounding our Milky Way, scientists on the Dark Energy Survey have been able to constrain the fundamental particle physics that governs dark matter.