Next-generation particle beam cooling experiment underway at Fermilab accelerator
- accelerator
- beam
- beam cooling
- electromagnet
- FAST
- Fermilab Accelerator Science and Technology Facility
- IOTA
- optical stochastic cooling
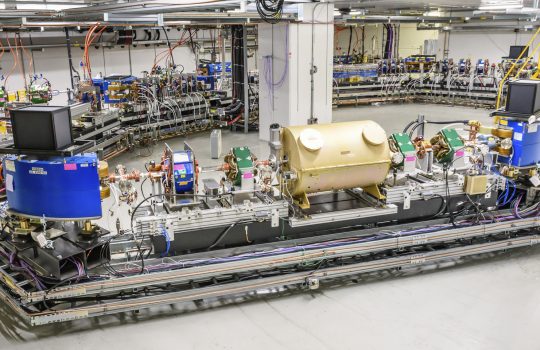
High-intensity particle beams enable researchers to probe rare physics phenomena. A proposed technique called optical stochastic cooling could achieve brighter beams 10,000 times faster than current technology allows. A proof-of-principle experiment to demonstrate OSC has begun at Fermilab’s Integrable Optics Test Accelerator.