Solid-state technology for big data in particle physics
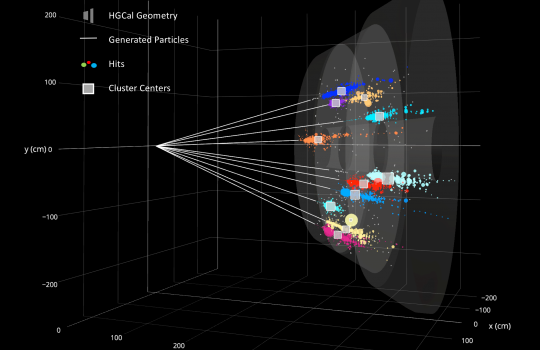
Scientists working on experiments at the LHC are continually refining our understanding of the fundamental constituents of our universe. Every measurement, every new, uncovered facet of a subatomic particle comes only after a thorough and rigorous analysis of the data. The way they access that data may soon get an upgrade at Fermilab, where CMS collaborators recently installed a new solid-state technology at its computing facility. The technology will complement the standard spinning-disk hard drives that have been the dominant computer storage devices for the last several decades.