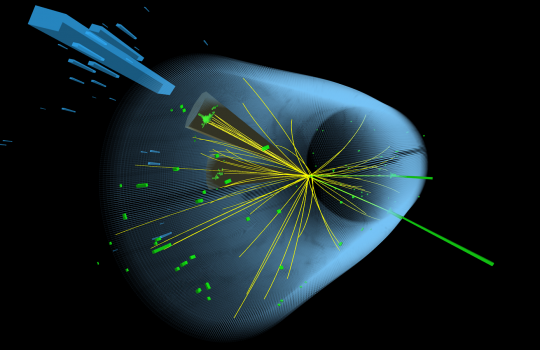
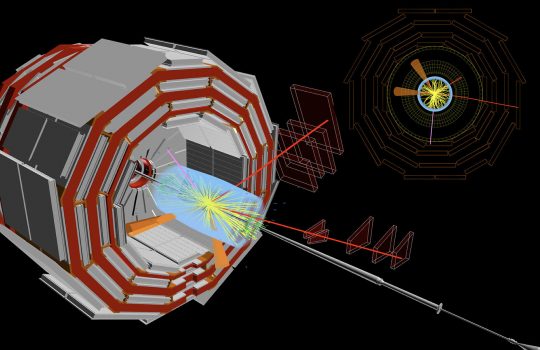
High-energy physics opens its doors to the exabyte era
From IRIS-HEP, April 10, 2021: Allison Hall, Fermilab LHC Physics Center researcher, is quoted in this story on the hardware upgrade to CERN’s Large LHC that will significantly boost the proton beams’ intensity.