Coffea speeds up particle physics data analysis
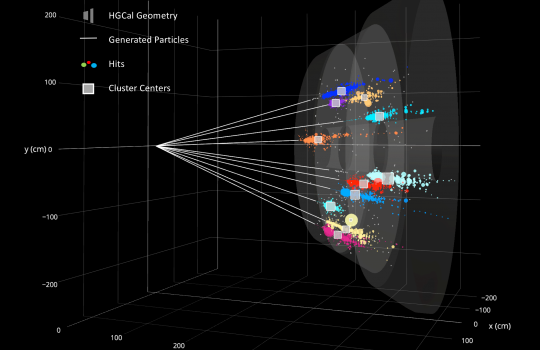
The prodigious amount of data produced at the Large Hadron Collider presents a major challenge for data analysis. Coffea, a Python package developed by Fermilab researchers, speeds up computation and helps scientists work more efficiently. Around a dozen international LHC research groups now use Coffea, which draws on big data techniques used outside physics.