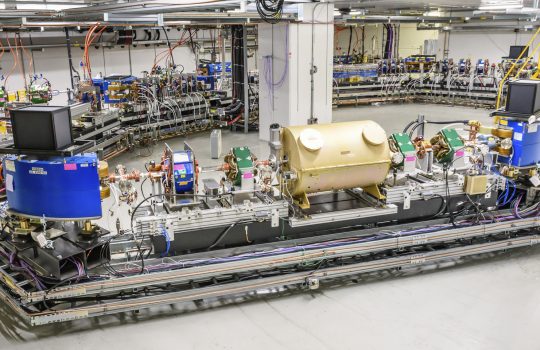
Which neutrino is the heaviest?
Figuring out which type of neutrino is heaviest, or solving the puzzle of neutrino mass hierarchy, would be a huge leap in our understanding of both neutrinos and the physics that govern our universe. The NoVA experiment or DUNE could help physicists do just that.